Each state as obtained as a solution of the Schrödinger equation of the hydrogen atom is
characterised by a unique combination of the quantum numbers n, l, and m.
We have seen that each state can be populated by up to two electrons. Even if we reduce the
energy of the system to near absolute zero temperature, not all of the electrons converge on
the n=1 state but remain in higher states because the n=1 state can't take more than
two electrons. This has lead to Pauli's exclusion principle: No two electrons can
share the same state (i.e. have the same quantum numbers) at the same time. Therefore,
we need another quantum number, spin, to distinguish the two electrons sharing the same
hydrogen, i.e. (n,l,m) state.
Here is an overview of the quantum numbers:

The main quantum number, n, determines the energy of the state (exactly in the case of hydrogen-like atoms; with minor corrections involving the other quantum numbers for multi-electron atoms). It also determines the size of the spherical envelope of the wave function: The higher n, the further the probability cloud stretches out into space. Possible values of n are positive integer numbers.
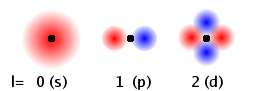
The angular momentum quantum number, l, governs the ellipticity of the probability cloud and the number of planar nodes going through the nucleus. In the Fig., red and blue areas indicate regions with opposite sign of the wave function and the black dot represents the position of the nucleus. For a given n, the possible values are integers from 0 up to n-1.
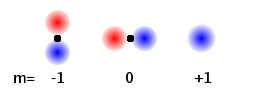
The magnetic quantum number, m, is related to the magnetic moment of any non-spherical electron (probability) distribution. Therefore, the different m states relate to differently orientated orbitals. Which one is which depends on the preferential axis, i.e. the orientation of an external field, if any. All (n,l) states with different m look the same. In the Fig., the third one is the same shape as the others but orientated perpendicular to the screen. The values of m for a given (n,l) range from -l to +l.
The spin (quantum number), s, is similar to l in that it refers to an angular momentum component. It can be visualised as the rotation of the electron, thought of as a particle, around its own axis rather than around the nucleus. This is, however, a bit of a crutch because the electron's behaviour has both aspects of particle (such as scattering) and wave (such as diffraction), and if carried through quantitatively doesn't give accurate results. The possible values of the spin quantum number are -½ and +½ for electrons.
Classical objects in great numbers can be treated by classical statistics, also known as Boltzmann statistics. This is the basis of properties such as temperature and pressure, which have little meaning for an individual submicroscopic particle but are properties of an ensemble of such particles. See 2nd year Thermal Physics for a discussion of Boltzmann statistics.
Quantum-mechanical particles obey a different sort of statistics which takes into account the discrete, quantised nature of physical properties on very small length scales. When the size of the objects making up the ensemble increases, the quantum statistics approach the classical limit, which is the familiar Boltzmann statistics. The classical description is not wrong, but it is not accurate enough to deal with the smallest of objects.
There are two different quantum statistics (the gory mathematical detail will be left for 3rd year Condensed Matter Physics). The Fermi-Dirac statistics applies to particles with half-integer spin (such as electrons). It is only for these Fermions that the exclusion principle applies. Bosons, particles with integer spin, have their own quantum statistics, Bose-Einstein statistics. Bosons have some quite counter-intuitive properties at extremely low temperatures which follow from the fact that all of them can occupy the same lowest-energy state. The helium isotope 3He, for example, is a superfluid, i.e. a fluid that flows without friction. This surprising behaviour is due to the condensation of the 3He atoms in the lowest energy state, a process known as Bose-Einstein condensation.
The components of angular momentum are quantised. This applies both to orbital angular momentum (quantum number l) and to spin (quantum number s).
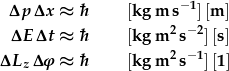
The uncertainty principle applies to all products of observables whose units combine to [J s] = [kg m2 s-1], i.e. the dimension of Planck's constant. The best-known uncertainty principle is the one linking the uncertainties of position, x, and momentum, p. We have also used the energy-time uncertainty principle when discussing energy bands.
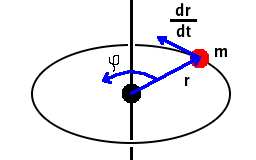
Angular momentum is a vector defined by the cross product
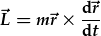 . Judging by its units,
[kg][m]×[m s-1]=[kg m2 s-1], the complementary uncertainty
should be dimensionless. It is in fact the uncertainty of the angle of rotation, φ.
. Judging by its units,
[kg][m]×[m s-1]=[kg m2 s-1], the complementary uncertainty
should be dimensionless. It is in fact the uncertainty of the angle of rotation, φ.
The uncertainty of the angle must be limited to 2π - the angular momentum has to point somewhere on a circular orbit. Therefore, the uncertainty of the component of the angular momentum perpendicular to the direction of motion must be of the order of Planck's constant. We may therefore conclude that values of Lz are quantised in multiples of h/2π.
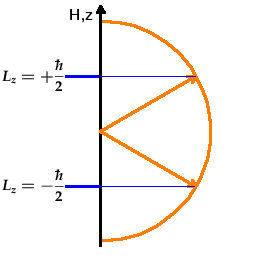
There are 2l+1 possible orientations of the angular momentum,
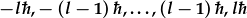 ,
and two possible orientations of the spin,
,
and two possible orientations of the spin,
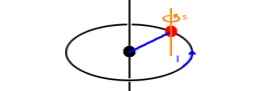
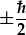 , of an electron. The Fig. shows the situation for
the spin: The spin aligns at an angle with the z axis (which could be a preferential axis generated by
applying a magnetic field or by a chemical bond). There are two possible orientations (these are
often called parallel or up and anti-parallel or down although
that's exactly what they are not!). The angle with the z axis is given by the need to distribute
the 2l+1 states uniformly over the whole angular range from the +z to the -z direction. For example,
in the case of an l=1 angular momentum state, there are three possible orientations, one of which
is perpendicular to the z axis, and the other two are 45o of the positive and negative z axis,
respectively. In no case is the angular momentum vector exactly (anti-)parallel to the z axis. If it was,
we would know both the angular momentum and the angle precisely, which would defy the uncertainty
principle.
, of an electron. The Fig. shows the situation for
the spin: The spin aligns at an angle with the z axis (which could be a preferential axis generated by
applying a magnetic field or by a chemical bond). There are two possible orientations (these are
often called parallel or up and anti-parallel or down although
that's exactly what they are not!). The angle with the z axis is given by the need to distribute
the 2l+1 states uniformly over the whole angular range from the +z to the -z direction. For example,
in the case of an l=1 angular momentum state, there are three possible orientations, one of which
is perpendicular to the z axis, and the other two are 45o of the positive and negative z axis,
respectively. In no case is the angular momentum vector exactly (anti-)parallel to the z axis. If it was,
we would know both the angular momentum and the angle precisely, which would defy the uncertainty
principle.