Boltzmann's entropy of a macrostate
$$S=k_B\ln\Omega$$
all microstates are equally probable
statistical weight of a macrostate, $\Omega$
$$S=-k_B\sum_ip_i\ln{p_i}$$
probability of a microstate, $p_i$
information
binary chunks: bits
information entropy
$$S=-\sum_i\log_2p_i\qquad\qquad\color{grey}{[\ln{x}=\ln{2}\cdot\log_2x]}$$
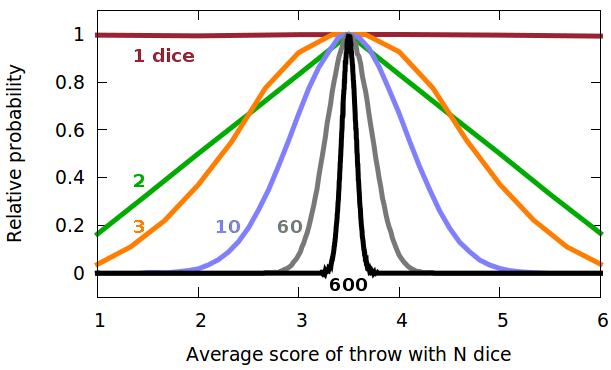
thermodynamics:
Gibbs's algorithm
$${\rm d}\ln{\Omega}\overset{!}{=}0$$
find the most probable macrostate
Gaussian (random) distribution
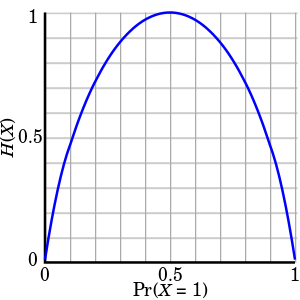
information theory:
find the information content of a message
arbitrary distribution functions
surprisal
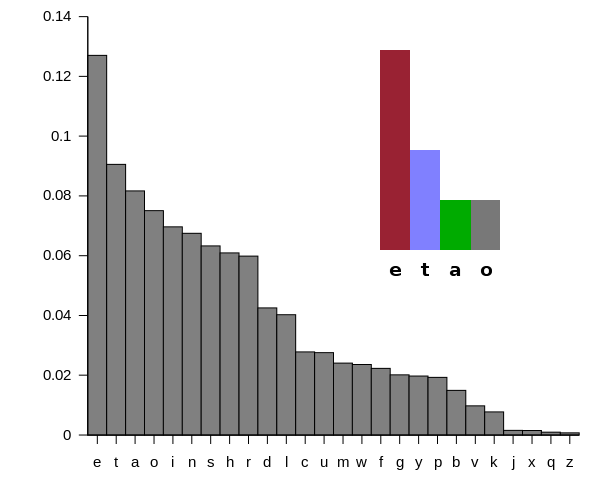
letter frequencies
surprisal of a particular letter
letter combinations: th, qu...
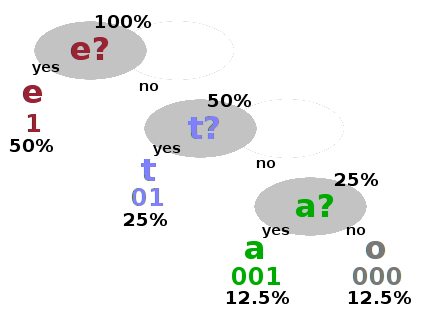
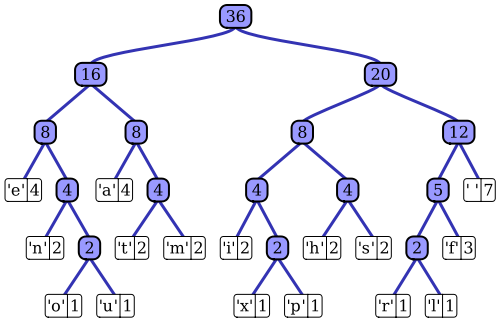
data compression
chain of binary decisions
Huffman encoding
Huffman tree
number of binary decisions needed = information entropy of message
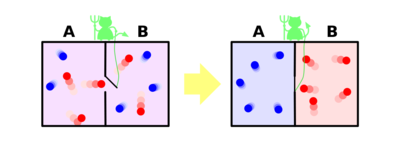
Maxwell's daemon
second law
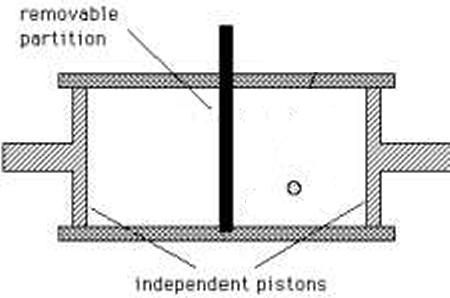
Szilard's engine
1 bit of information destroyed
$$k_BT\ln{2}$$
work extracted
Case study:
S Toyabe, T Sagawa, M Ueda, E Muneyuki, M Sano
Information heat engine: converting information to energy by feedback control
Nature Phys 6 (2010) 988
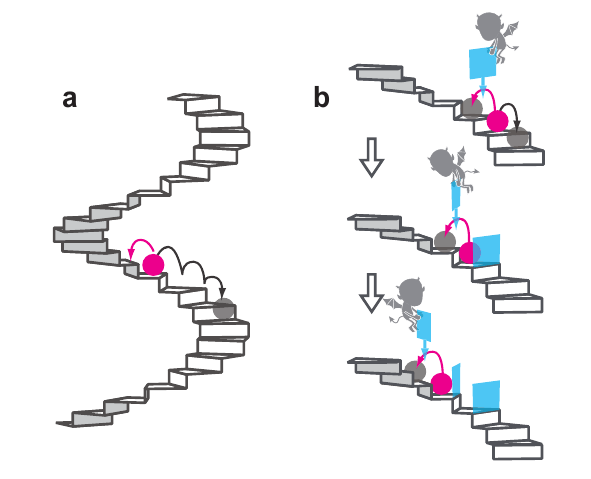
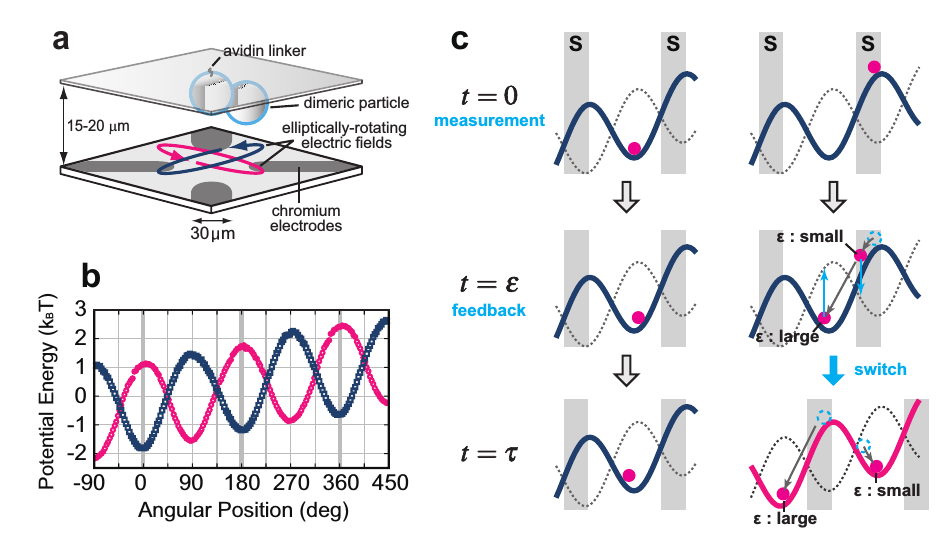
information heat engine
Landauer's principle